
Not all software faults are caused by coding errors. A single fault may result in a wide range of failure symptoms. Examples of these changes in environment include the software being run on a new computer hardware platform, alterations in source data, or interacting with different software. A fault that did not reveal failures may result in a failure when the environment is changed.
#Software system designer test code
For example, faults in the dead code will never result in failures. Not all faults will necessarily result in failures. If this fault is executed, in certain situations the system will produce wrong results, causing a failure. Software faults occur through the following process: A programmer makes an error (mistake), which results in a fault (defect, bug) in the software source code. Software testing assists in making this assessment. Therefore, when an organization develops or otherwise invests in a software product, it can assess whether the software product will be acceptable to its end users, its target audience, its purchasers, and other stakeholders. For example, the audience for video game software is completely different from banking software. : 41–43Įvery software product has a target audience. Information derived from software testing may be used to correct the process by which software is developed. There are various roles for testing team members. In the current culture of software development, a testing organization may be separate from the development team. The scope of software testing may include the examination of code as well as the execution of that code in various environments and conditions as well as examining the aspects of code: does it do what it is supposed to do and do what it needs to do. Testing cannot establish that a product functions properly under all conditions, but only that it does not function properly under specific conditions.
These oracles may include (but are not limited to) specifications, contracts, comparable products, past versions of the same product, inferences about intended or expected purpose, user or customer expectations, relevant standards, applicable laws, or other criteria.Ī primary purpose of testing is to detect software failures so that defects may be discovered and corrected. Instead, it furnishes a criticism or comparison that compares the state and behavior of the product against test oracles - principles or mechanisms by which someone might recognize a problem. Software testing can determine the correctness of software under the assumption of some specific hypotheses (see the hierarchy of testing difficulty below), testing cannot identify all the failures within the software. Software testing can provide objective, independent information about the quality of software and risk of its failure to users or sponsors.
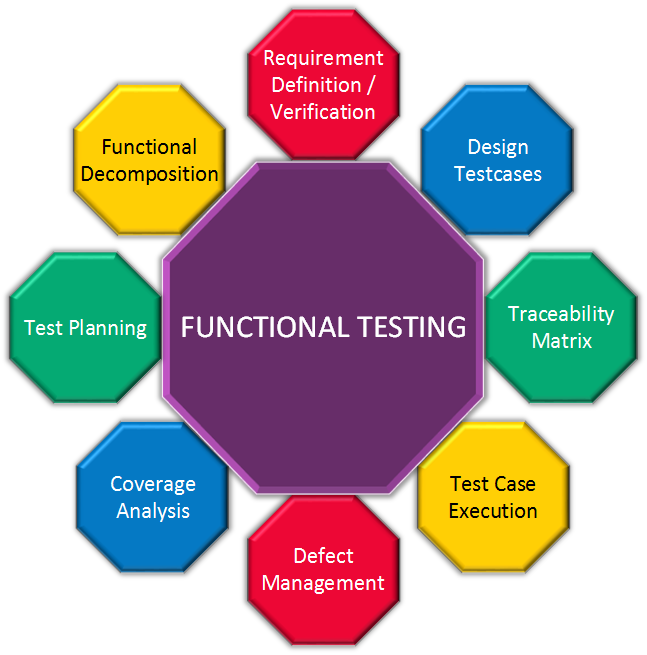
executing a program or application with the intent of examining behavior.working with product developers on improvement in coding techniques, design patterns, tests that can be written as part of code based on various techniques like boundary conditions, etc.reviewing the product architecture and the overall design of the product.analyzing the product requirements for completeness and correctness in various contexts like industry perspective, business perspective, feasibility and viability of implementation, usability, performance, security, infrastructure considerations, etc.Test techniques include, but are not necessarily limited to: Software testing can also provide an objective, independent view of the software to allow the business to appreciate and understand the risks of software implementation.

Software testing is the act of examining the artifacts and the behavior of the software under test by validation and verification.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
